Priming is an approach that
involves treating seeds with different organic or inorganic chemicals. Seed
priming treatment occurs before sowing seeds. This seed treatment involves
soaking the seeds in various solutions for a specified duration under controlled
conditions. It is followed by drying the seeds to their original moisture
content to prevent premature radicle emergence before sowing. This process
stimulates various metabolic processes that enhance germination and mitigate
the detrimental effects of seed damage. Seed priming is one way to overcome
several constraints effectively. It is a simple, low-cost, low-risk
intervention that can assist farmers with their livelihoods by improving crop
emergence, development, and productivity.
Seed priming Methods:
Hydropriming ,
osmopriming,
Drum priming,
solid matrix priming,
Biopriming,
Hormonal priming,
Nanopriming,
Physical priming,
Halopriming
Nutripriming
Nutripriming involves applying nutrients in a solution to enhance
seed quality by increasing the nutrient content of the seed. Micronutrients are
essential for plant growth, playing crucial roles in photosynthesis and
respiration. Micronutrients can be applied in three ways: soil application,
foliar application to leaves, or direct seed application. Direct seed treatment
is the most effective option for improving seedling growth and micronutrients. Zinc
(Zn) is one of the primary micro-nutrients essential for plant growth and
production since plants need Zn in small amounts for various enzymes and
protein activities. The average range of Zn required by plants is 15-55 ppm.
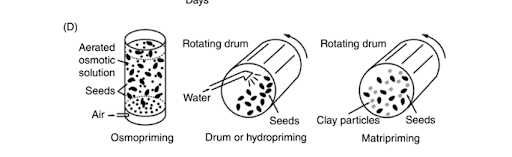
Hydropriming
Seeds are soaked in water and
dried before sowing. Soaking by submerging seeds in water can be performed with
or without aeration.
Osmopriming, Matricondioning,
drum priming
Seeds are primed in osmotic
solution.
Matricondioning,
Seeds primed in moist solid
carrier materials.
Drum priming
Seeds are primed in water.
Solid matrix priming
It is same as hydro priming but
it used solid medium like vermiculite,
calcium silicate, or calcined clay. It's an alternative to osmotic priming
(using liquid solutions) because it requires less volume of solution and better
aeration.
Biopriming
In this method seeds are treated
with beneficial microbes. They protect plants from harmful pathogens. For
example pseudomonas-aided zinc application or zinc seed priming with endophytic
bacteria improved the productivity of bread wheat.
Hormonal priming
Phytohormones such as cytokinin (CK) , Auxin (IAA),
gibberellin (GA), Abscisic (ABA), ethylene (ET), salicyclic acid (SA) are
essential for plant growth and development. Hormonal priming involves the use
of phytohormones in the priming medium. Plant growth regulators have been found
effective in improving the crop performance under optimal and suboptimal growth
condition. For instance ABA is a phytohormone
involved in a number of abiotic stresses, such as osmotic, low
temperature and drought stress.
Nano priming
Nano priming involves the
application of nanomaterials such as metal and metal oxide nanoparticles to
seeds prior to germination.
Nanoparticles can be categorized
into different types based on their composition such as metal nanoparticles
(gold,silver,iron), metal oxide nanoparticles (titanium dioxide, zinc oxide),
semiconductor nanoparticles( quantum dots), carbon-based nanoparticles (carbon
nanotubes, graphene). Nano priming can improve the establishment of seedlings,
increase biomass production. The specific effects of nanopriming can vary deending on the type of
nanomaterials used, their concentration, the timing and the duration of
application, as well as the specific plant species and environmental condition.
At low concentration, Se has a positive effect on crop growth and stress
tolerance.
Physical priming
Physical treatment are good
alternatives to raise agricultural production along with improvement in plant
protection and post-treatment. Electromagnetic priming is ecofriendly , cheap
and noninvasive technique.
Another physical agent ionizing radiation like gamma rays is
a powerful mutagenic tool in agricultural sciences.seed irradiation with gamma
rays at doses lower than 100 GY can
enhance germination percentage.